

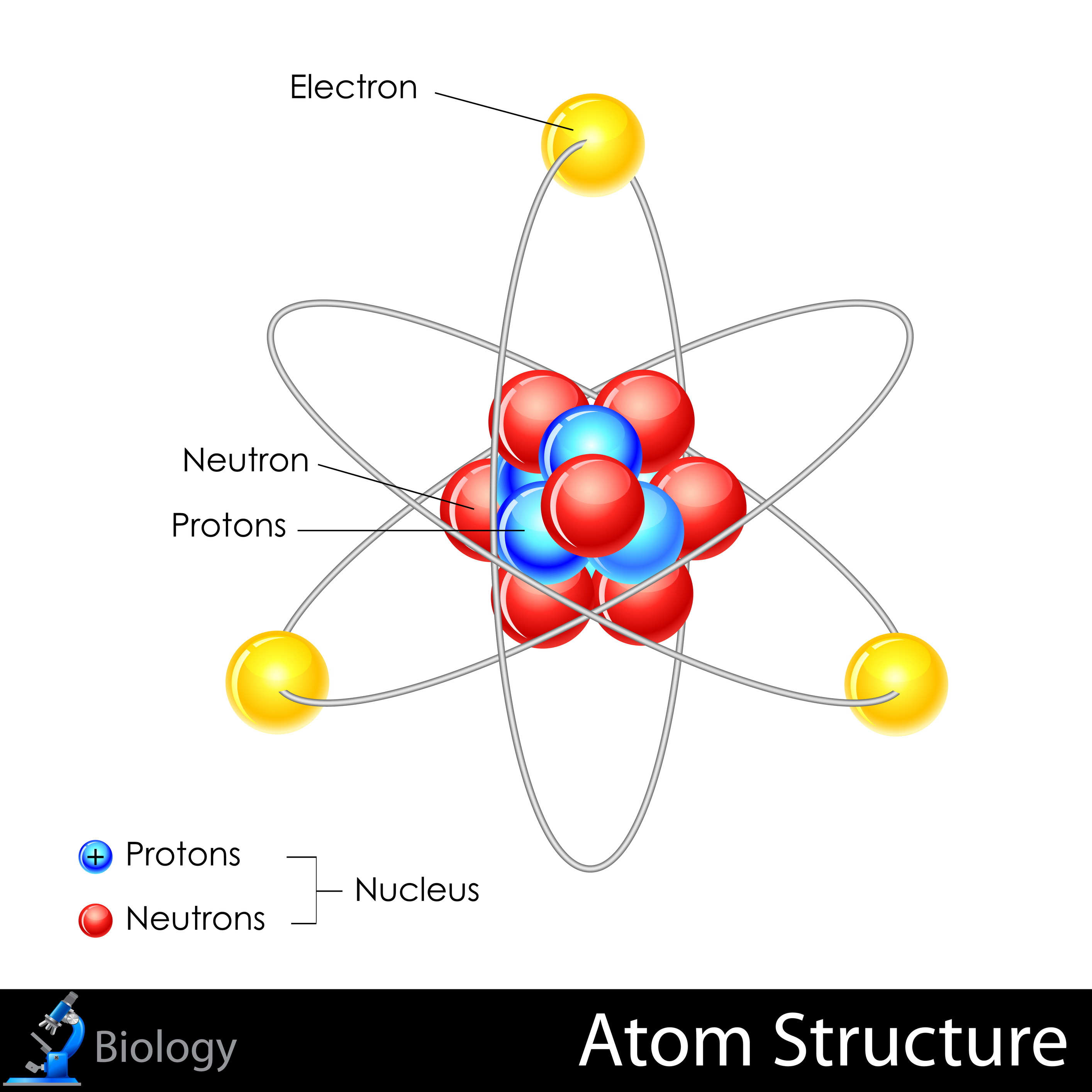
Their model should change between the two to show that mastery of the standard has been met. Modeling is accomplished by students making a concept map (CM) of the atomic structure that illustrates their understanding based on prior knowledge and then after formal notes have been presented to them. The students explore the atom using two of the NGSS Practices: (1) Questioning and (2) Developing and Using Models. This is aligned with the NGSS Disciplinary Core Idea (DCI) PS1.A ( Structure and Properties of Matter): “each atom has a charged substructure consisting of a nucleus, which is made of protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons”. The goal of the lesson is to introduce students to the basic structure of the atom, its sub atomic parts, their charges and the relative size of the atom. The tremendous energy of the sun which is obtained by nuclear fusion, releases trillions of neutrino every second.This lesson addresses the NGSS HS-PS1-1, "use the periodic table as a model to predict the relative properties of elements based on the patterns of electrons in the outermost energy level of atoms". Neutrino has no charge but travels at a very high speed, similar to the speed of light, and can pass through any solid object.
Gluons: Also found within protons and electrons, they act as exchange particles that help transfer strong force between quarks.A proton contains three quarks (two up quarks and one down quark), whereas a neutron contains (two down quarks and one up quark). Quarks are of six different types: up, down, top, bottom, charm, and strange.

However, their exact position in an atom cannot be measured with accuracy. They were independently discovered by Murray Gell-Mann and George Zweig in 1964. Quarks: They are fundamental subatomic particles that makeup protons and electrons.Given below is a table showing the charge, mass, and location of the three sub-atomic particles: Name of the Particle Neutrons are neutral particles with no charge but have a substantial size and mass similar to a proton. They were discovered by James Chadwick in the year 1932 and are denoted by the symbol n or n 0. Neutrons, similar to protons, are made of quarks and gluons. They are also found within the nucleus along with the protons in a tightly packed manner. Protons consist of even smaller particles called quarks and gluons.įound tightly packed with the nucleus, they make up virtually all of the mass of an atom along with the neutrons. They were discovered by Ernest Rutherford in the year 1917 and are denoted by the symbol p or p +. Protons are positively charged particles found within a dense region at the center of the atom called the nucleus. When the number of negatively charged electrons is equal to the number of positively charged protons, the atom is neutral in charge. Thomson discovered it in the year 1897.Įlectrons move so fast around the nucleus that their exact location within an atom cannot be determined with accuracy. The standard symbol used for an electron is e or e –. Unlike protons and neutrons, electrons are fundamental particles much smaller (almost 1800 times) in size than protons and neutrons. They are negatively charged particles that revolve around the nucleus in a fixed orbit. In contrast, electrons are found outside the nucleus in a region called the electron cloud or electron shell. Electrons and protons are found at the center of the atom within a dense region called the nucleus. All atoms except hydrogen contain three basic subatomic particles: 1) electrons, 2) protons, and neutrons.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
